

- How to identify compromised computer wireshark pcap code#
- How to identify compromised computer wireshark pcap download#
How to identify compromised computer wireshark pcap download#
Lets follow tcp stream 2įrom above snippet we can see that attacker is trying to download a file using ftp connection and on following tcp stream 3 we can seeįrom above we can conclude protocol used for downloading malware Q10. Since we only have 5 TCP streams, the easiest way is to follow each TCP stream.
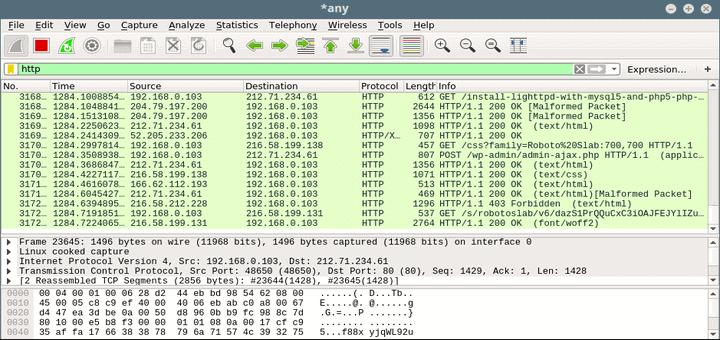
Hint: Refer explanation for question 7 Q9: Which protocol did the attacker use to download additional malicious files to the target system? If you have come this far, this question should not pose any challenge. Q8:Which protocol was used to carry over the exploit? Note: Do not move ahead without understanding this particular point. Next we will do google-search to check for any known vulnerabilities related to DsROLEUpgradeDownLevelServer and you will get the answer to the question.Now we can assume that the above command will some how help the attacker in exploiting the victim.From the attacker we see “ DsROLEUpgradeDownLevelServer request“.We see Bind_ACK from the server meaning it will accept execution of remote code.
How to identify compromised computer wireshark pcap code#
In short we can say that client can execute code remotely on the server via this protocol. After that, the client can request calls to the server. A client will call this endpoint mapper and ask for a specific interface, which will be accessed on a different connection. A DCE/RPC server’s endpoint mapper (EPMAP) will listen for incoming calls. Before moving ahead lets understand what this meansĭistributed Computing Environment/Remote Procedure Call (DCE/RPC)ĭCE/RPC is a specification for a remote procedure call mechanism that defines both APIs and an over-the-network protocol.
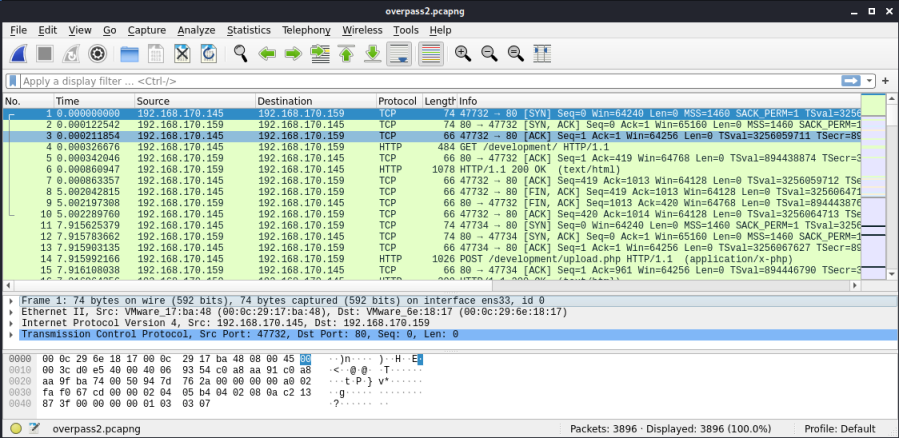
To get the answer, filter by smb protocol and then move to the packet where you can see NTLM_CHALLENGE and you will get the answer under Session Setup and Response. Also, you can add Stream Index column and then sort it in descending order as shown below Q5:How long did it take to perform the attack (in seconds)?Īgain refer to the Conversations window and you will get the answer under IPv4 tab->Duration Q6: What is the operating system of the target host? The easiest way to answer this question is to refer to the TCP tab in conversations window. Q4:How many TCP sessions are present in the captured traffic? Since we have the public IP of the attacker we can easily track the geo location by any Geo-IP tracker tool available online. Q2: What is the target’s IP address?įrom above we can conclude easily conclude that the target ip is 192.150.11.111 Q3: Provide the country code for the attacker’s IP address (a.k.a geo-location). Now 2 things stand out here 98.114.205.102, a public IP is making a SMB connection with 192.150.11.111, a internal server and from this we can conclude the attacker ip. In the above snippet we can see that 98.114.205.102 is initiating a TCP handshake with 192.150.11.111. Now, lets jump into the questions Q1 : What is the attacker’s IP address? This was probably used for downloading dataįrom the above point we can make a reasonable guess that attacker used SMB protocol to make a connection and then used RPC to execute code remotely. PacketMaze Challenge: Part 2 Wireshark Pcap analysis


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
